Urinary Catheterization: Complete Guide to Treatment and Care
Comprehensive guide to urinary catheterization, types, uses, and management of urological problems. Learn about insertion procedures, care, benefits, and risks.
Urinary Catheterization: Complete Guide to Treatment and Care
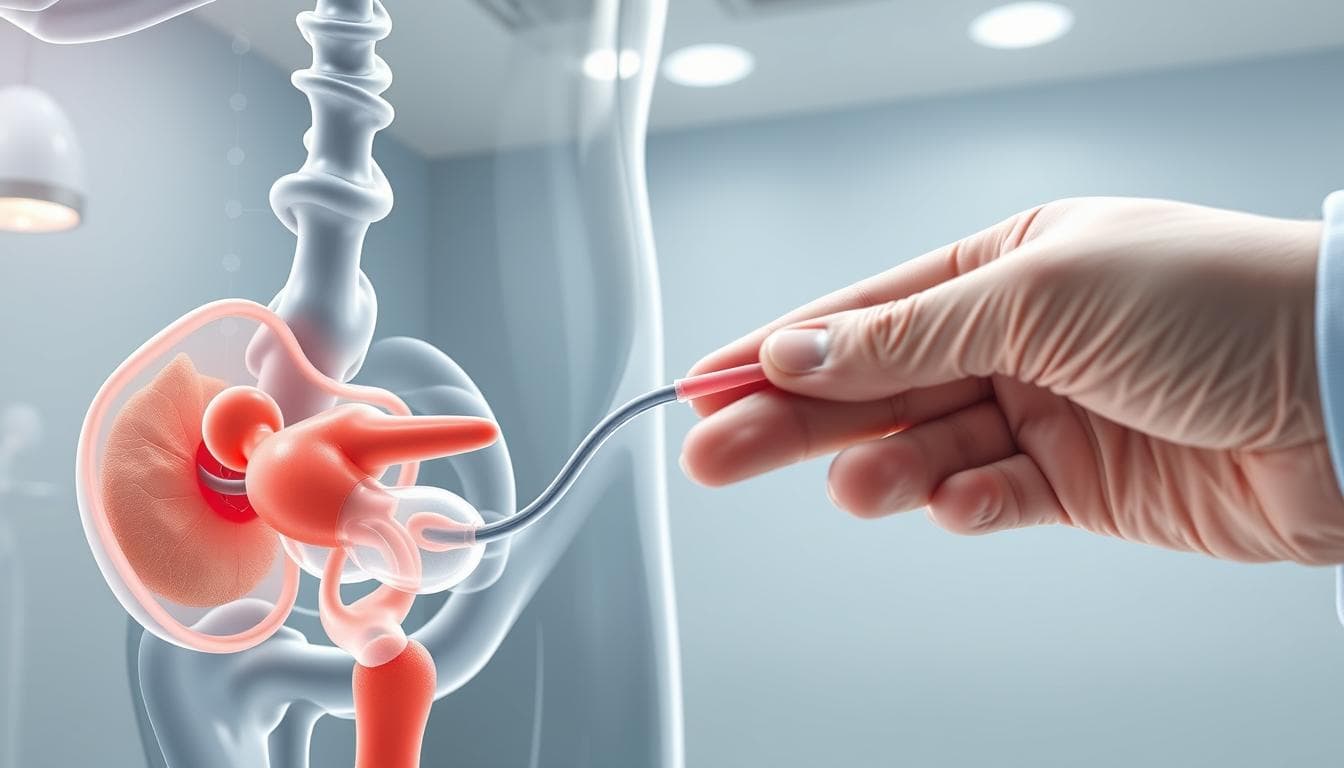
Urinary catheterization is an important medical procedure that helps treat many urological problems. It is used to drain urine from the bladder when a patient has difficulty urinating normally.

This procedure can be temporary or permanent, depending on the patient's condition. Urinary catheterization helps relieve pain and symptoms associated with urination problems, thereby improving patients' quality of life.
Urinary catheterization is considered a safe and effective procedure in treating urological problems.
Key Takeaways
- Urinary catheterization helps treat urological problems
- Used to drain urine from the bladder
- Can be temporary or permanent
- Helps relieve pain and symptoms
- Improves patients' quality of life
Overview of the Urinary System and Common Problems
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, all working together to filter blood and excrete urine. Each part of these components plays a vital role in maintaining body health.
Anatomy of the Urinary System
The urinary system consists of several main organs: the kidneys that filter blood and produce urine, the ureters that transport urine to the bladder, the bladder that stores urine, and the urethra through which urine is excreted outside the body. All these parts work in harmony to ensure proper urinary system function.
Common Urological Problems
There are many problems that can affect the urinary system, including urinary retention which can be acute or chronic, and urinary tract infections that may occur in any part of the urinary system. These problems can lead to symptoms such as pain during urination, urgent need to urinate, and blood in urine.
It is important to recognize these problems early to ensure effective treatment and avoid complications. Treatments may include using urinary catheterization in some cases to improve urine drainage and relieve symptoms.
Urinary Catheterization: Definition and Medical Importance
Urinary catheterization plays a vital role in modern medicine by facilitating urine drainage and relieving symptoms associated with urological problems. This medical procedure has a long history and continuous development, making it an essential tool in treating many medical conditions.
What is Urinary Catheterization
Urinary catheterization is a medical procedure in which a thin, flexible tube is inserted through the urethra into the bladder to drain urine. It is used to treat urinary retention, relieve pain caused by bladder fullness, and monitor urine output. Urinary catheterization can be temporary or permanent, depending on the patient's medical condition.
Historical Development of Urinary Catheterization
The history of urinary catheterization dates back to ancient times, when primitive tools were used to drain urine. With medical advancement, the materials and techniques used in catheterization evolved, increasing its effectiveness and safety. Today, urinary catheterization is used in a wide range of medical applications, from critical care to long-term management of urological problems.
Importance of Catheterization in Modern Medicine
Urinary catheterization has become a vital tool in modern medicine due to its ability to improve quality of life for patients suffering from urological problems. By facilitating urine drainage, catheterization reduces the risk of infection and other complications associated with urinary retention. It also plays an important role in palliative care for patients suffering from chronic diseases.
| Use | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary retention | Draining urine from bladder | Pain relief, reduced infection risk |
| Urine monitoring | Measuring urine output | Kidney function monitoring, patient assessment |
| Chronic conditions | Long-term management of urological problems | Improved quality of life, reduced complications |
Different Types of Urinary Catheters
Urinary catheterization is an important medical tool, available in multiple types to suit different medical conditions. A urinary catheter is a thin tube inserted through the urethra into the bladder to drain urine. It is used in multiple cases, such as urinary retention, bladder diseases, and after surgical operations.
Temporary Urinary Catheter
Temporary urinary catheter is used for a specific time period and is usually removed once the patient's condition improves.
When to Use
Temporary urinary catheter is used in cases such as surgical operations or when there is temporary urinary retention.
Advantages
The advantages of temporary urinary catheter include reducing the risk of urinary tract infection compared to permanent catheterization, and allowing the patient to return to normal life quickly.
Permanent Urinary Catheter
Permanent urinary catheter is used for a long period and requires periodic replacement.
Foley Catheter and Its Characteristics
Foley catheter is a type of permanent urinary catheter, distinguished by having a small balloon that maintains catheter stability in the bladder.
Advantages of Foley catheter:
- Provides continuous urine drainage
- Easy installation and maintenance
- Reduces leakage risk
Other Specialized Catheter Types
There are other specialized catheter types, such as external catheter (condom) for men, which is used as an alternative to internal catheterization in some cases.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/3iwpWYfjXXE" title="Urinary Catheterization and Medical Care" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>The appropriate catheter is chosen based on the patient's medical condition and individual needs.
Medical Conditions Requiring Urinary Catheterization
Urinary catheterization is resorted to in cases of acute and chronic urinary retention and other diseases related to the urinary system. Urinary catheterization plays a vital role in managing many medical conditions related to the urinary system.
Acute and Chronic Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a medical condition characterized by inability to completely empty the bladder. Urinary retention can be acute or chronic, requiring urinary catheterization in both cases to ensure proper urine drainage.
Post-Surgical Procedures
After some surgical operations, patients may need to use urinary catheterization temporarily to ensure no urological complications occur. This procedure helps maintain patient health and reduce potential risks.
Chronic Urinary System Diseases
There are many chronic urinary system diseases that may require urinary catheterization, including:
Prostate Enlargement
Prostate enlargement can lead to urinary retention, necessitating urinary catheterization to relieve symptoms.
Neurological Injuries
Neurological injuries can affect bladder function, potentially requiring urinary catheterization for urination management.
Other Conditions
There are other conditions such as tumors or chronic inflammations that may require urinary catheterization.
| Medical Condition | Description | Urinary Catheterization Use |
|---|---|---|
| Acute and chronic urinary retention | Inability to completely empty bladder | Necessary for urine drainage |
| Post-surgical procedures | Need for catheterization after surgery | Temporary to avoid complications |
| Prostate enlargement | Impact on urine flow | To relieve symptoms |
Urinary Catheter Insertion Procedures Step by Step
Urinary catheter insertion requires precise knowledge of correct procedures and techniques to ensure patient safety and avoid complications.
Necessary Preparations Before Procedure
Before starting urinary catheter insertion, several preparatory procedures must be taken:
- Assess patient's general health condition
- Determine appropriate catheter type
- Provide sterile environment for procedure
Urinary Catheter Insertion Technique
Catheter insertion technique differs between men and women due to anatomical differences.
For Men
For catheter insertion in men, the following steps are followed:
- Clean the area thoroughly
- Use local anesthetic to reduce pain
- Gently insert catheter through urethra
For Women
For catheter insertion in women, the following steps are followed:
- Position patient appropriately
- Clean area around urethra
- Gently insert catheter
Direct Care After Catheter Insertion
After catheter insertion, follow-up care procedures must be followed to ensure no complications occur.
It is important to monitor the patient regularly to ensure there are no signs of infection or other complications.
The patient must also be taught how to properly care for the catheter.
| Care | Description |
|---|---|
| Catheter cleaning | Catheter should be cleaned daily with soap and water |
| Catheter replacement | Catheter should be replaced periodically according to doctor's instructions |
Benefits and Advantages of Urinary Catheter Use
Urinary catheterization plays an important role in relieving symptoms associated with urological problems. Through urinary catheter use, patients can overcome many health challenges that affect their daily lives.
Relieving Medical Symptoms
Urinary catheterization helps relieve pain and discomfort resulting from urinary retention. It also reduces the risk of urinary tract infection due to proper urine drainage.
- Reduce pain resulting from urinary retention
- Reduce risk of urinary tract infection
- Improve sleep ability by reducing frequent urination need
Improving Patients' Quality of Life
Using urinary catheterization can significantly improve patients' quality of life. By allowing them to perform daily activities without fear of urinary accidents.
Patients who use urinary catheterization often feel improvement in their daily lives, as they can:
- Participate in social activities without worry
- Exercise more easily
- Enjoy peaceful and comfortable sleep
Potential Risks and Complications of Urinary Catheterization
Urinary catheterization, despite its benefits, carries risks and complications that must be well understood. These complications can range from urinary tract infection to urethral injuries, in addition to psychological and social effects.
Urinary Tract Infection: Causes and Prevention
Urinary tract infection is one of the most common complications of urinary catheter use. Infection can occur due to catheter contamination or failure to follow proper hygiene procedures.
- Follow strict sterilization procedures when inserting catheter
- Change catheter regularly according to doctor's instructions
- Monitor infection signs such as fever or pain
Potential Urethral Injuries
Urethral injuries can occur during catheter insertion or removal. These injuries may lead to bleeding or pain.
To prevent urethral injuries:
- Catheter insertion should be performed by trained professionals
- Use appropriate lubricants to facilitate catheter insertion
Psychological and Social Complications
Using urinary catheterization can affect the patient's psychological state, potentially leading to feelings of anxiety or depression.
To alleviate these complications:
- Provide psychological support to patient
- Educate patient about how to deal with catheter
In conclusion, it is important for patients to be aware of potential risks and complications of urinary catheterization. By understanding these risks and taking preventive measures, complications can be reduced and quality of life improved.
Daily Care of Urinary Catheter
Good hygiene is the key to preventing complications when using urinary catheterization. Daily care of urinary catheter is no less important than the procedure itself to ensure patient health and comfort.
Daily Hygiene Protocol
Patients who use urinary catheterization must follow a daily hygiene routine. This includes washing hands thoroughly before touching the catheter and cleaning the area around the catheter using mild soap and warm water.
Daily hygiene steps:
- Wash hands thoroughly before touching catheter
- Clean area around catheter
- Avoid using harsh chemicals
Catheter Replacement and Maintenance Schedule
Changing the catheter periodically is an essential part of caring for it. A doctor should be consulted to determine the appropriate schedule for catheter replacement.
| Category | Replacement Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Temporary catheter | Weekly | Depends on patient condition |
| Permanent catheter | Every 4-6 weeks | Doctor consultation required |
Strategies for Complication Prevention
To prevent complications, patients should monitor any unusual changes in urine or pain sensation. Good hydration should also be maintained by drinking sufficient amounts of water.
Additionally, some additional strategies can be followed such as avoiding pressure on the catheter and avoiding bending it.
Adapting to Daily Life with Urinary Catheter
Life with urinary catheterization requires balance between dealing with psychological challenges and enjoying daily activities. Adapting to catheterization can be challenging, but with the right advice, it can become part of daily routine.
Dealing with Psychological Challenges
Having urinary catheterization may lead to psychological challenges such as anxiety or depression. It is important to talk to a mental health specialist to deal with these challenges. Relaxation and meditation techniques can help reduce anxiety.
Performing Daily Activities and Exercise
Daily activities and exercise can be easily performed with urinary catheterization. It is recommended to wear comfortable clothing and secure the catheter properly during movement. Light sports such as walking or swimming can be practiced.
| Activity | Safety Tips |
|---|---|
| Walking | Ensure catheter is securely fastened |
| Swimming | Use waterproof bag for catheter |
Practical Tips for Patients and Their Families
Patients and their families must understand how to deal with catheterization properly. This includes learning how to change and clean the catheter regularly. A specialized nurse visit can help provide necessary support.

Treatment Alternatives to Urinary Catheterization
While urinary catheterization is considered an effective solution for some urological problems, there are other treatment alternatives that may be suitable. In some cases, these alternatives may be safer or more comfortable for patients.
Available Medication Treatments
Medication treatments are one of the available options as an alternative to urinary catheterization. These treatments may include medications that help improve urine flow or reduce symptoms associated with urological problems. Doctor consultation is required to determine the appropriate medication for each case.
Alternative Surgical Options
In some cases, surgery may be an alternative to urinary catheterization. Surgical procedures include repairing or widening the urethra, or removing obstacles that impede urine flow. Each case must be evaluated individually to determine if surgery is appropriate.
Complementary and Natural Treatments
There are also complementary and natural treatments that can help improve urological symptoms. These treatments include lifestyle changes, such as dietary modification and increased physical activity.
Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Consultation
Patients who use urinary catheterization should be aware of warning signs that require immediate medical attention. These signs may indicate serious health problems requiring rapid response.
Urinary Tract Infection Indicators
Urinary tract infection is one of the common complications of urinary catheter use. Warning signs of urinary tract infection include: fever, pain during urination, and urine color change. If you notice any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Urine Drainage Problems
Urine drainage problems may occur due to catheter blockage or displacement. Signs include: decreased urine amount, pain in lower abdomen, and swelling around catheter. These problems require immediate medical attention to avoid complications.
Unusual Pain or Bleeding
Unusual pain or bleeding during or after urinary catheter use may be a sign of health problem. Patients experiencing these symptoms should seek medical help immediately.
Special Considerations for Different Patient Groups
Urinary catheterization requires a customized approach according to individual patient needs, especially when dealing with elderly, children, and patients with special needs.
Urinary Catheterization for Elderly
Elderly often suffer from multiple health problems, making urinary catheter use require special considerations. It is important to assess the general health condition of elderly and determine if urinary catheterization is the optimal choice for them.
- Assess mobility and independence ability
- Consider chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease
- Provide necessary support and care for effective catheter management
Urinary Catheterization for Children
When it comes to children, care should be more detailed and adapted to their special needs. Using urinary catheterization for children requires sensitivity and special attention.
- Assess child's general health condition
- Choose appropriate catheter size
- Provide psychological and educational support for child and parents
Patients with Special Needs
Patients with special needs may require specialized care when using urinary catheterization. It is important to consider their individual needs and provide necessary support.
Some important considerations include:
- Provide comfortable and safe environment
- Train caregivers on proper catheter handling
- Monitor patient's health condition regularly

Recent Technological Developments in Urinary Catheterization
The field of urinary catheterization has witnessed tremendous technological developments in recent years. These developments aim to improve patient experience and reduce complications associated with urinary catheter use.
Innovations in Catheter Design
New catheters have been designed with improved characteristics to reduce friction and facilitate insertion and removal. Some of these innovations include:
- Catheters with soft tips to reduce pain during insertion
- Catheters with antimicrobial coating to reduce infection risk
- Catheters adaptable to individual patient anatomy
New Body-Friendly Materials
Materials used in catheter manufacturing have become more advanced and body-friendly. Some of these materials include:
| Material | Characteristics | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Silicone | Flexible, non-toxic | Reduce bladder irritation |
| Hydrogel | Moisturizing, reduces friction | Reduce pain during insertion and removal |
Conclusion
Urinary catheterization is an important medical procedure that helps treat many urological problems. Through this article, we learned about different types of urinary catheters, medical conditions requiring their use, and insertion procedures.
The medical importance of urinary catheterization is shown in relieving medical symptoms and improving patients' quality of life. However, it is essential for patients to be aware of potential risks and complications, such as urinary tract infection and urethral injuries.
To deal with urinary catheterization effectively, daily hygiene protocols must be followed, along with catheter replacement and maintenance schedules. Adapting to daily life with catheterization also requires understanding how to deal with psychological challenges and social ones.
In conclusion, urinary catheterization is a valuable medical tool, but it must be used carefully and following doctors' instructions to ensure patient safety and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is urinary catheterization?
Urinary catheterization is a medical procedure in which a thin tube is inserted through the urethra into the bladder to drain urine.
When is urinary catheterization used?
Urinary catheterization is used in cases of urinary retention, after surgical operations, and in some chronic medical conditions such as prostate enlargement.
What are the types of urinary catheters?
There are several types of urinary catheters, including temporary catheter, permanent catheter, and Foley catheter.
How is urinary catheter inserted?
Urinary catheter insertion is performed by healthcare specialist, where the catheter is inserted through the urethra into the bladder.
What are the potential risks of urinary catheter use?
Potential risks include urinary tract infection, urethral injuries, and psychological and social complications.
How can I care for urinary catheter?
Daily hygiene protocol should be followed, catheter should be changed regularly, and doctor's instructions should be followed.
Can I perform daily activities with urinary catheter?
Yes, daily activities can be performed, but doctor's advice and guidance should be followed.
What are the warning signs requiring medical consultation?
Warning signs include urinary tract infection indicators, urine drainage problems, and unusual pain or bleeding.
Additional Sources and References
Additional Information
Need Help?
Our specialized medical team is available to provide assistance and medical consultations


